Cortex-M4/M4F Implementation
4 days classroom training.
This classroom course includes training materials, lunch, coffee and snacks.
Request more information
Lena Bernhardsson – SE, DK, NO
+46 (0) 40 59 22 09
lena.bernhardsson@nohau.se
Heidi Lehtomäki – Finland
phone: +358 40 196 0142
heidi.lehtomaki@nohau.fi
Klaus Ahrensbach – Denmark
Phone: +45 3116 1019
ka@nohau.dk
The participants will acquire understanding in intricacies of ARM Cortex-M4 family – its architecture, programming, exception handling & debugging and hardware implementation.
Instructed by an embedded professional with over decades of experience in embedded software engineering, this training course provides the participants with professional competence to work in serious embedded development projects.
The trainees gain valuable resources for working in real embedded engineering projects, along with printed material that can be as reference afterwards.
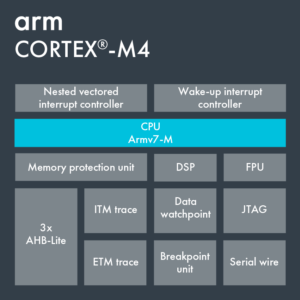
The course covers three separate parts:
- Cortex-M4 architecture
- Cortex-M4 software implementation and debug
- Cortex-M4 hardware implementation
- While Cortex-M4 seems to be a simple 32-bit core, it features sophisticated mechanisms, such as exception pre-emption, internal bus matrix and debug units
- The Cortex-M4 low level programming will explained, particularly the ARM linker parameterizing and some important assembly instructions
- The DSP and FPU instructions to boost DSP algorithm implementation is introduced, featuring the hardware implementation and providing some guidelines to SoC –based design on Cortex-M4.
- An overview of the ARM CoreSight specification is provided prior to describing the debug related units
- A basic understanding of microprocessors and microcontrollers is required
- Adequate programming skills
- Printed training material provided during the training course
- Comprehensive and easy to use, allowing for later usability as a reference material
- After the course, each trainee receives a completion certificate signed by the trainer
Introduction to ARM Cortex-M4
- ARM Cortex-M4 processor macrocell
- Programmer’s model
- Instruction pipeline
- Fixed memory map
- Privilege, modes and stacks
- Memory Protection Unit
- Interrupt handling
- Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller [NVIC]
- Power management
- Debug
ARM Cortex-M4 core
- Special purpose registers
- Datapath and pipeline
- Write buffer
- Bit-banding
- System timer
- State, privilege and stacks
- System control block
Architecture of a SoC based on Cortex-M4
- Internal bus matrix
- External bus matrix to support DMA masters
- Connecting peripherals
- Sharing resources between Cortex-M4 and other CPUs
- Connection to Power Manager Controller
Embedded Software Development with Cortex-M4
- Application startup
- Placing code, data, stack and heap in the memory map, scatterloading
- Reset and initialization
- Placing a minimal vector table
- Further memory map considerations, 8-byte stack alignment in handlers
THUMB-2 Instruction Set
- General points on syntax
- Data processing instructions
- Branch and control flow instructions
- Memory access instructions
- Exception generating instructions
- If…then conditional blocks
- Stack in operation
- Exclusive load and store instructions, implementing atomic sequences
- Memory barriers and synchronization
Cortex-M4 DSP Instruction Set
- Multiply instructions
- Packing / unpacking instructions
- V6 ARM SIMD packed add / sub instructions
- SIMD combined add/sub instructions, implementing canonical complex operations
- Multiply and multiply accumulate instructions
- SIMD sum absolute difference instructions
- SIMD select instruction
- Saturation instructions
Floating Point Unit
- Introduction to IEEE754
- Floating point arithmetic
- Cortex-M4F single precision FPU
- Register bank
- Enabling the FPU
- FPU performance, fused MAC
- Improving the performance by selection flush-to-zero mode and default NaN mode
- Extension of AAPCS to include FP registers
C/C++ Compiler Hints & Tips for Cortex-M4
- Mixing C/C++ and assembly
- Coding with ARM compiler
- Measuring stack usage
- Unaligned accesses
- Local and global data issues, alignment of structures
- Further optimizations, linker feedback
Interrupts
- Basic interrupt operation, micro-coded interrupt mechanism
- Interrupt entry / exit, timing diagrams
- Interrupt stack
- Tail chaining
- Interrupt response, pre-emption
- Interrupt prioritization
- Interrupt handlers
Memory Protection Unit
- Memory types
- Access order
- Memory barriers, self-modifying code
- Memory protection overview, ARM v7 PMSA
- Cortex-M4 MPU and bus faults
- Fault status and address registers
- Region overview, memory type and access control, sub-regions
- Region overlapping
Invasive Debug
- CoreSight debug infrastructure
- Halt mode
- Vector catching
- Debug event sources
- Flash patch and breakpoint features
- Data watchpoint and trace
- ARM debug interface specification
- CoreSight components
- AHB-Access Port
- Possible DP implementations: Serial Wire, JTAG Debug Port [SWJ-DP] or SW-DP
Non-Invasive debug
- Basic ETM operation
- Instruction trace principles
- Instrumentation trace macrocell
- ITM stimulus port registers
- DWT trace packets
- Hardware event types
- Instruction tracing
- Synchronization packets
- Interface between on-chip trace data from ETM and Instrumentation Trace Macrocell [ITM]
- TPIU components
- Serial Wire connection
AMBA3.0 Interconnect Specification
- Purpose of this specification
- Example of SoC based on AMBA specification
- Differences between AMBA2.0 and AMBA3.0
AHB – Advanced High-Performance Bus
- Centralized address decoding
- Address gating logic
- Arbitration, bus parking
- Indivisible transactions
- Single-data transactions
- Address pipelining
- Sequential transfers
- AHB-lite specification
- Parameterizing the AHB core provided by ARM
APB – Advanced Peripheral Bus
- Second-level address decoding
- Read timing diagram
- Write timing diagram
- Operation of the AHB-to-APB bridge
- 0 new features
AHB Cortex-M4 Hardware Implementation
- Clocking and reset, power management
- Using an external Wake-up Interrupt Controller (WIC)
- Bus interfaces: Icode memory interface, Dcode memory interface, System interface and External Private Peripheral Bus interface
- AMBA-3 compliance
- Unifying the code buses
- Unaligned access management
- Debug interface
- Connection to the TPIU
- AHB Trace Macrocell (HTM)